Importance Of Serial Dilution In Serology Tests
A serial dilution is the stepwise of a in. Usually the at each step is constant, resulting in a of the in a fashion. A ten-fold serial dilution could be 1, 0.1 M, 0.01 M, 0.001 M.
- Importance Of Serial Dilution In Serology Tests 1
- Importance Of Serial Dilution In Serology Tests Online
Oct 19, 2011 Serial dilution is a simple yet efficient technique to determine the number of cells or organisms in a concentrated sample. First, take a portion of the sample and does serial dilution on it. Repeat the steps until the cells can be observed under the microscope when the. The Advantages of Serial Dilution. Some techniques operate and are applicable to a wide range of concentrations of the species in question. Preparing a series of solutions to generate a calibration curve of instrument response is fairly labor intensive and provides many points where errors may occur. By performing two-fold serial dilutions on the serum prior to testing, the concentration of the serum antibodies can be expressed as an HI titre to the log base 2. Standardization of the HI test. It is important that there is correlation between the results of tests carried out by different technicians and in different laboratories.
Serial dilutions are used to accurately create highly diluted solutions as well as solutions for resulting in with a. A tenfold dilution for each step is called a logarithmic dilution or log-dilution, a 3.16-fold (10 0.5-fold) dilution is called a half-logarithmic dilution or half-log dilution, and a 1.78-fold (10 0.25-fold) dilution is called a quarter-logarithmic dilution or quarter-log dilution. Serial dilutions are widely used in experimental sciences, including, and.
Contents. In biology and medicine In and, besides the more conventional uses described above, serial dilution may also be used to reduce the concentration of microscopic organisms or cells in a sample. As, for instance, the number and size of that grow on an plate in a given time is concentration-dependent, and since many other diagnostic techniques involve physically counting the number of micro-organisms or cells on specials printed with grids (for comparing concentrations of two organisms or cell types in the sample) or wells of a given volume (for absolute concentrations), dilution can be useful for getting more manageable results. Serial dilution is also a cheaper and simpler method for preparing than and. In homeopathy. Experiments in Microbiology, Plant Pathology and Biotechnology.
New Age Publishers, 2005, p. Booth, C.; et al. Methods in microbiology 35. Academic Press. Weissmann, Gerald (2006). The FASEB Journal.
20 (11): 1755–1758. Retrieved 2008-02-01. Ernst, Edzard (November 2005). 'Is homeopathy a clinically valuable approach?' Trends in Pharmacological Sciences.
26 (11): 547–548. Bishop, Edward P.
Fody, Larry E. Clinical Chemistry: Principles, Procedures, Correlations. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2004, p. 24. External links., Bates College.
This article does not any. Unsourced material may be challenged and.
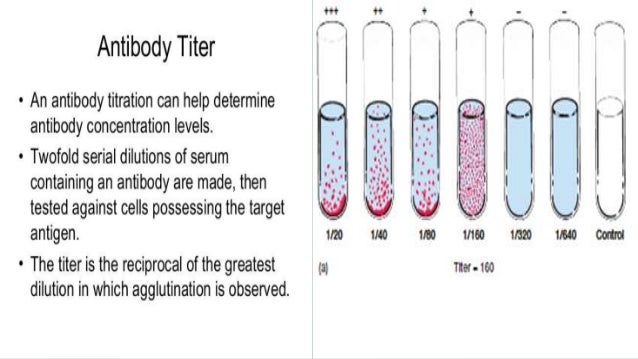
(January 2009) An antibody is a measurement of how much an organism has produced that recognizes a particular, expressed as the inverse of the greatest dilution (in a ) that still gives a positive result. Is a common means of determining antibody titers.
For example, the detects the presence of anti-Rh antibodies in a pregnant woman's. A patient might be reported to have an 'indirect Coombs titer' of 16.
Importance Of Serial Dilution In Serology Tests 1
This means that the patient's serum gives a positive indirect Coombs test at any dilution down to 1/16 (1 part serum to 15 parts diluent). At greater dilutions the indirect Coombs test is negative. If a few weeks later the same patient had an indirect Coombs titer of 32 (1/32 dilution which is 1 part serum to 31 parts diluent), this would mean that she was making more anti-Rh antibody, since it took a greater dilution to abolish the positive test.
Many traditional tests such as or employ this principle. Such tests can typically be read visually, which makes them fast and cost-effective in a 'low-tech' environment.
Importance Of Serial Dilution In Serology Tests Online
The interpretation of serological titers is guided by that are specific to the or in question; a titer of 1:32 may be below the cut-off for one test but above for another.